Fiber Optics, Connecting the World
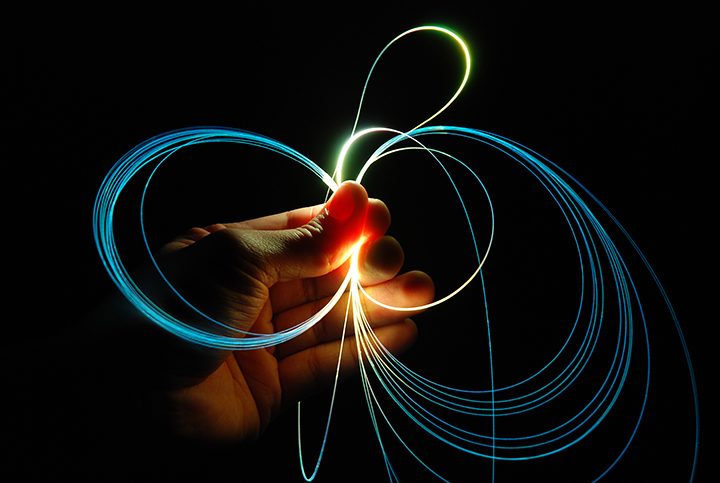
Image Credit: Optoelectronics Research Centre, Southampton, UK
Optical fibers, hair-thin flexible strands of glass or plastic, have revolutionized our world. Because of their capacity to carry massive amounts of data in the form of light, optical fibers serve as the backbone of the Internet. Almost every video and photo you download and nearly every email and text you send travels over optical fiber, sometimes across the world. The ability to transport confined light inside bent fibers means that they can also be used in endoscopes for imaging the interiors of both people and machines. As fiber lasers, they can generate and conveniently direct light energy for cutting everything from human tissue to thick steel. Remote source lighting uses optical fiber to deliver light from a conveniently located central source to a distant user. The newest optical fiber has one or more hollow cores in which the light travels in air, allowing applications undreamed of just a decade ago.
Download high-res image file | Download caption as .zip file
La fibra óptica, conectando al mundo:
Las fibras ópticas, hebras de vidrio o plástico flexible del grosor de un cabello, han revolucionado nuestro mundo. Por su capacidad para llevar cantidades masivas de datos en forma de luz, la fibra óptica es la columna vertebral del internet. Casi cualquier video y foto que descargas, así como cualquier correo electrónico y texto que envías, viaja a través de fibra óptica, algunas veces por el mundo.
La habilidad para transportar luz confinada dentro de fibras dobladas, implica que también puedan ser usadas en endoscopios para obtener imágenes del interior de máquinas y personas. Como fibras láser, pueden generar y dirigir convenientemente la energía de la luz para cortar cualquier cosa, desde tejido humano hasta acero. Las fuentes remotas de iluminación usan fibra óptica para entregar luz de una fuente central a un usuario distante. Las nuevas fibras ópticas tienen uno o más núcleos huecos en los que la luz viaja en el aire, permitiendo aplicaciones impensables hace una década.
Download high-res image file | Download caption as .zip file
Die Glasfaser
Glasfasern sind haarfeine flexible Stränge aus Glas oder Kunststoff, die unsere Welt revolutioniert haben. Aufgrund ihrer Fähigkeit, große Datenmengen in Form von Licht zu übertragen, sind Lichtleitfasern quasi das Rückgrat des Internets. Fast jeder Video- und Fotodownload und fast jede E-Mail und jeder Text, den sie verschicken, reist per Glasfaser durch die ganze Welt. Die Fähigkeit, Licht beschränkt im Inneren von gebogenen Fasern transportieren zu können, führt dazu, dass sie auch in Endoskopen zur Erfassung der Innenräume von Menschen und Maschinen verwendet werden. Bei Lasern können sie zur Umleitung direkter Lichtenergie für das Schneiden, von menschlichem Gewebe bis zu dickem Stahl, verwendet werden. Fernlichtquellen könnten durch Glasfasern Licht von einer günstig gelegen zentralen Quelle zu einem entfernten Benutzer liefern. In der neuesten Glasfasertechnologie werden Glasfasern mit einem oder mehreren Hohlkernen verwendet, in denen sich das Licht in der Luft fortbewegt und so werden neue Anwendungen möglich, von denen man vor einigen Jahren nur träumen konnte.
Download high-res image file | Download caption as .zip file



